Pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a general term that refers to an infection of the female internal reproductive organs. PID may be used synonymously with the following terms:
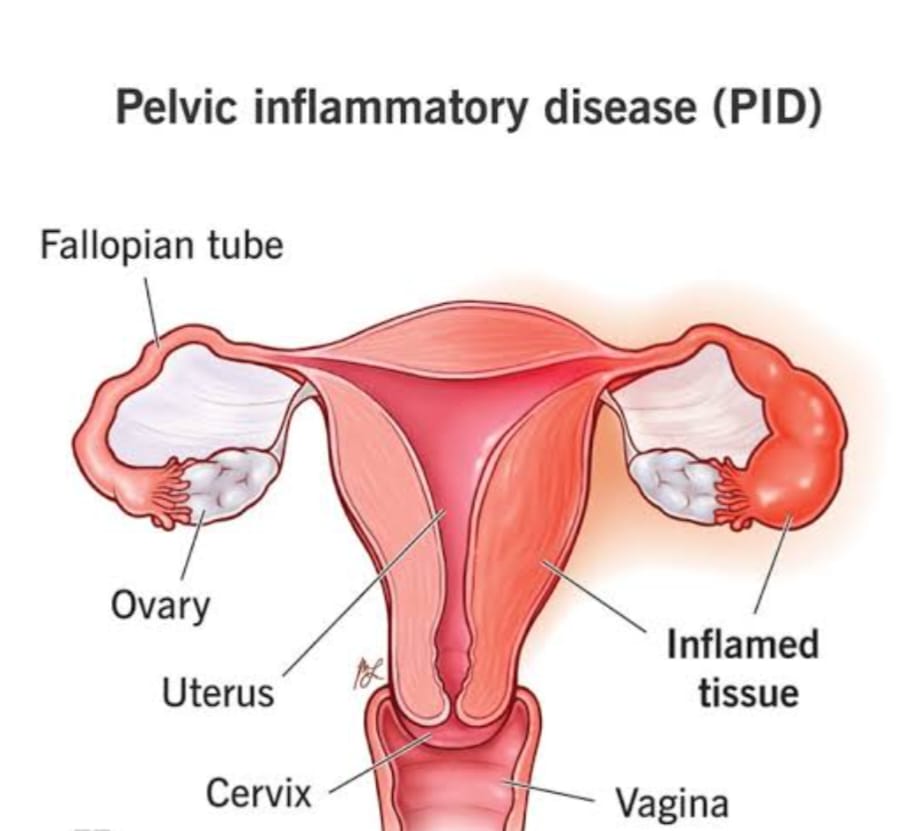
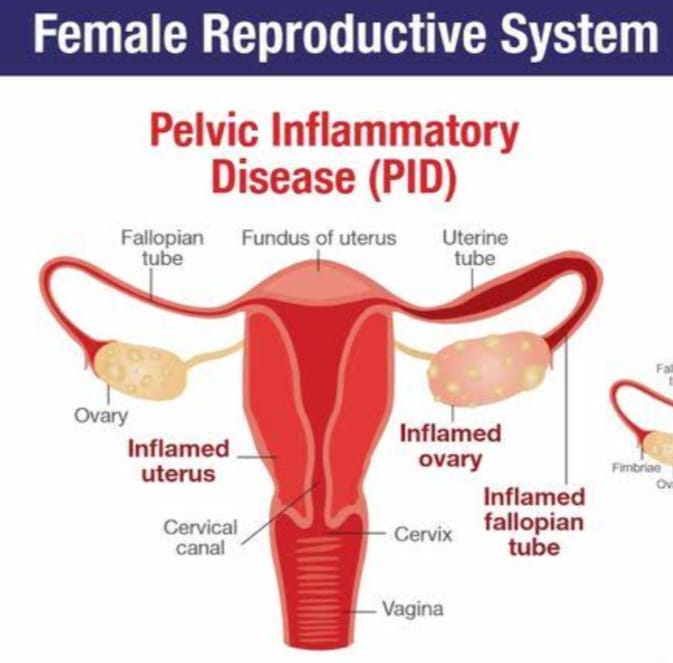
Salpingitis: inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Endometritis: Inflammation of the inside lining of the body of the uterus.
Tubo-ovarian abscesses: abscesses in the tubes and ovaries. Pelvic peritonitis: inflammation inside of the abdominal cavity surrounding the female reproductive organs.
It is a common and serious contagious if it is caused by a sexually transmitted organism (STDs). PID can involve the fallopian tubes, cervix, uterus, ovaries, and urinary bladder and can cause serious damage if left untreated.
It affects sexually active females after puberty, especially late teens and early 20`s. Each year India only, it is estimated that more than 1 million women experience an episode of acute PID. More than 100,000 women become infertile each year as a result of PID, and a large proportion of the ectopic pregnancies occurring every year are due to the consequences of PID. Annually more than 150 women die from PID or its complications.
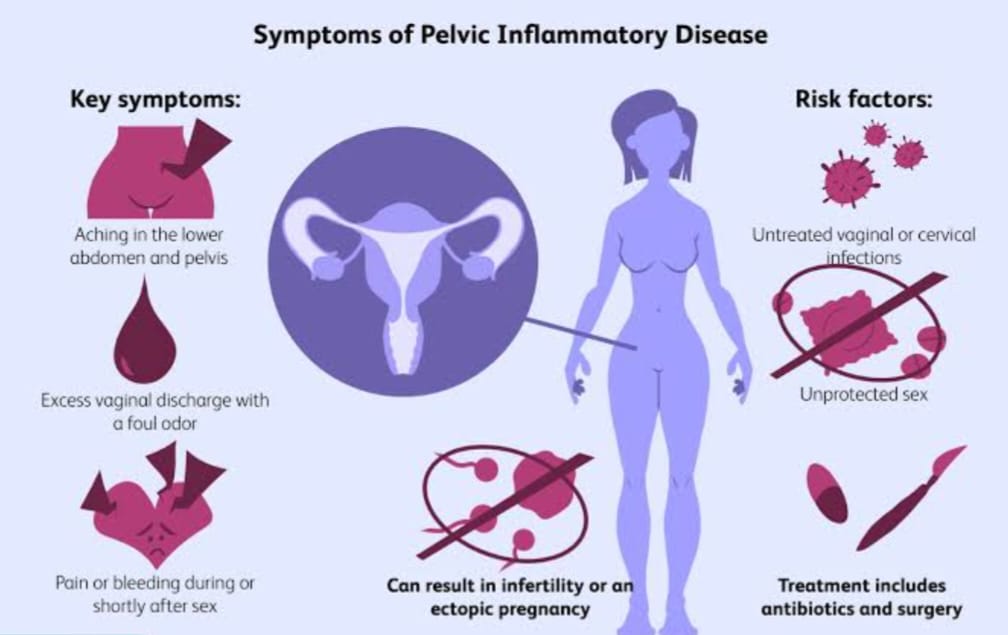
Symptoms of PID varies.
When PID is caused by chlamydial infection, a woman may experience mild symptoms or no symptoms at all, while serious damage is being done to her reproductive organs. Because of vague symptoms, PID goes unrecognized by women and their health care providers about two thirds of the time.
Early symptoms (up to 1 week):
Pain in the lower pelvis on one or both sides.
Pain with intercourse.
Bad-smelling vaginal discharge.
General ill feeling.
Backache.
Low fever.
Frequent, painful urination.
Irregular menstrual bleeding.
Later symptoms (1 to 3 weeks later):
Severe pain and tenderness in the lower abdomen.
High fever
Foul smelling vaginal discharge.
Causes:-
Bacterial infection ( chlamydial, gonorrheal, or mycoplasmal) or a virus. This may be transmitted by an infected sexual partner. Childbirth, spontaneous or induced abortion, or use of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD) are all conditions that may alter or weaken the normal lining cells, making them susceptible to infection, usually by several organisms. During menstruation, the cervix widens and may allow pathogens entry into the uterine cavity. Pelvic surgery.
Sometimes PID can occur after the cervix is treated because of an abnormal Pap smear. POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
Prompt and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications of PID. Without treatment, PID can cause permanent damage to the female reproductive organs. Pelvic abscess and rupture. This can be life-threatening Adhesions inside the pelvis
Female infertility
Ectopic pregnancy
Miscarriage
Recurrence
Chronic pelvic pain.
Diagnostic tests
Laboratory blood studies and culture of the vaginal discharge. A positive C-reactive protein (CRP) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
The ligase chain reaction (LCR) technique. The LCR technique detects DNA from N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis in a patient`s urine sample Pelvic Ultrasound
Laparoscopy
Caldocentesis (passage of a needle through the cervix into the peritoneal cavity to obtain a fluid sample).
HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENTS
Homeopathic remedy should be complementary to antibiotic therapy.
Homeopathic remedies offer immediate relief from symptoms . It is better equipped to quickly eradicate the infection. Help the body fights the disease and relieve painful symptoms associated with PID.
Helps to increase effectiveness of immune system. They are extremely effective when used following an attack in order to prevent a recurrence.
HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINE IS STRONGLY RECOMMENDED FOR PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE.